This is my final article in the Trashing the Ocean series. It looks at the results of the first major international effort to deal with the issue in 11 years. It’s less than satisfying effort largely due to the plastics lobby. One of the unofficial solutions: buy local and create local, sustainable communities says the guy who ‘discovered’ the pacific garbage patch. — Stephen
There are three to six kilogrammes of marine trash for every kilogramme of plankton…. California nearly became the first U.S. state to ban plastic bags, but a multi-million-dollar lobby effort by industry killed the proposed legislation
By Stephen Leahy
HONOLULU, Hawaii, U.S., Mar 28, 2011 (IPS)
Every day, billions of plastic bags and bottles are discarded, and every day, millions of these become plastic pollution, fouling the oceans and endangering marine life.
No one wants this, but there is wide disagreement about how to stop it.
“Every time I stick my nose in the water, I am shocked. I see less and less fish and more and more garbage,” said Jean-Michel Cousteau, son of the legendary marine ecologist Jacques Cousteau, who has spent four decades making documentaries and educating people about the oceans.
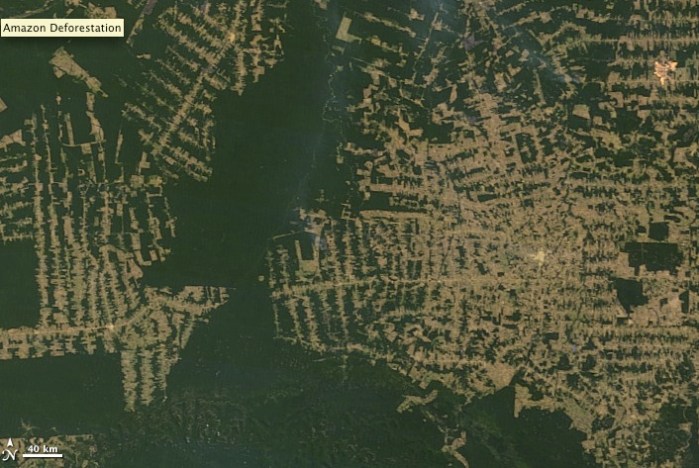
On trips to the remote and uninhabited northwestern Hawaiian Islands, Cousteau found miles and miles of plastic bottles, cigarette lighters, television tubes, spray cans, broken toys, and thousands of other pieces of plastic on the beaches and thousands of tonnes of derelict fishing nets in the reefs.
“We are using the oceans as a universal sewer,” he told some 440 participants from the plastics manufacturing, food and beverage sectors, environmental organisations, scientists and policy-makers from over 35 countries at the Fifth International Marine Debris Conference in Honolulu, Hawaii, which ended Mar. 25.

This independent environmental journalism depends on public support. Click here learn more.
Humanity is risking its own health and survival in treating the oceans this way, Cousteau said. The oceans are the source of life on our planet. Through evaporation, oceans are the most important source of fresh water while phytoplankton generates at least half the oxygen we breathe.
“No one is away from the ocean. We are all intimately connected by every breath we take,” he said.