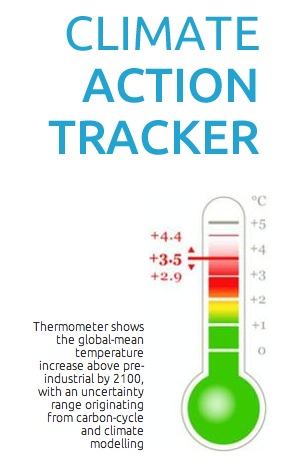
Climate change plays a role in all extreme weather now – atmosphere is 0.8C hotter and 4-6% wetter – turns out small increases can have big impacts. — Stephen
Stephen Leahy, International Environmental Journalist
By Stephen Leahy
CAIRNS, Australia, Apr 3, 2012 (Tierramérica)
Extreme weather is fast becoming the new normal. Canada and much of the United States experienced summer temperatures during winter this year, confirming the findings of a new report on extreme weather.
For two weeks this March most of North America baked under extraordinarily warm temperatures that melted all the snow and ice and broke 150-year-old temperature records by large margins.
Last year the U.S. endured 14 separate billion-dollar-plus weather disasters including flooding, hurricanes and tornados.
A new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), released Mar. 28, provides solid evidence that record-breaking weather events are increasing in number and becoming more extreme. And if current rates of greenhouse gas emissions are maintained, these events will reach dangerous new levels over the coming century.
Since 1950 there have been many more heat waves and record warm temperatures than in…
View original post 768 more words